3 Signs and signals
- 3.1 General
- 3.1.1 Light signals
- 3.1.1.1 Main signals
- 3.1.1.2 Approach signals
- 3.1.1.3 Shunt signals
- 3.1.2 Sign signals
- 3.1.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
- 3.1.2.2 Station stop signs
- 3.1.2.3 Stop signs
- 3.2 Japan
- 3.2.1 Light signals
- 3.2.1.1 Main signals
- 3.2.1.2 Approach signals
- 3.2.1.3 Other light signals
- 3.2.2 Sign signals
- 3.2.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
- 3.2.2.2 Station stop signs
- 3.2.2.3 Other sign signals
- 3.3 USA
- 3.3.1 New York subway
- 3.3.1.1 Light signals
- 3.3.1.1.1 Main signals
- 3.3.1.1.2 Other light signals
- 3.3.1.2 Sign signals
- 3.3.1.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
- 3.3.1.2.2 Station stop signs and stop signs
- 3.3.1.2.3 Other sign signals
- 3.3.2 Railway lines
- 3.3.2.1 Light signals
- 3.3.2.1.1 Main signals
- 3.3.2.2 Sign signals
- 3.3.2.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
- 3.3.2.2.2 Stop signs
- 3.3.2.2.3 Other sign signals
3.1 General
Various signals are of paramount importance for the safety of railroad and light rail traffic. The look and function of the signals differs between nations, and sometimes also differs within a nation depending on which company the line belongs to.
A motorman/engineer may, however, fail to obey a signal. Because of that, visible signals are often combined with automatic systems that will prevent accidents by slowing down or stopping the train if necessary. Such a system is the Japanese version of ATS, which can be simulated in BVE.
Signals in general can be divided into signal apparatus (commonly light signals), signal tools (such as a stop flag) and sign signals.
3.1.1 Light signals
Light signals are main signals, approach signals or shunt signals or a combination of these.
3.1.1.1 Main signals
Main signals show an aspect that may mean stop, proceed or proceed with caution/speed restriction. The meaning of the signal aspect is in effect from that place of the line where the signal is located.
![]()
Picture 1: Swedish main light signal aspect indicating Proceed at maximum 40
km/h, short route set
3.1.1.2 Distant signals
Approach signals, a.k.a. distant signals or relay signals, shows an aspect telling the aspect of a main signal ahead and beyond the approach signal. Distant signals are used at locations where the main signal cannot be seen at necessary distance. That may be because of obstacles in the line-of-sight to that main signal, or at lines where trains may travel at such a speed that the main signal cannot be seen from the place where the train must start slowing down if the main signal shows stop/danger or another restriction.
![]()
Picture 2: Japanese approach light signal aspect indicating Next main signal shows a speed
restriction
The aspect of an approach signal is always just a message of what aspect a main signal ahead shows. If the approach signal shows that the main signal ahead shows stop/danger, you should stop short of the main signal, not short of the approach signal.
3.1.1.3 Shunt signals
Shunt signals are often rather small and placed on/near the ground. Their signal aspects control shunting and such activities. They may, sometimes, also function as main signals. Shunt signals are rarely/never seen in BVE.
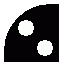
Picture 3: Swedish shunt signal aspect indicating Shunt movement allowed, obstacles present
3.1.2 Sign signals
Sign signals are located by the track, never changing aspect.
Common sign signals are permissible speed indicators telling the maximum allowed speed, platform stop markers showing where trains should stop at stations or stops or signs telling where to sound the horn/whistle.
3.1.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
Regarding permissible speed indicators, it should be remembered that if it indicates a speed greater than before that sign, the whole train should pass the sign before the higher speed is applied.
3.1.2.2 Station stop signs
A station stop sign tells where a passenger train should stop if it should stop at a station allowing passengers to embark/debark the train. The purposes of these signs are that:
- The train should stop without fouling another track
- All of the train should stop by the platform
- Short trains should not stop at the forward end of the platform requiring passengers waiting at the other end of the platform to walk a distance to embark the train
The simplest arrangement is when there is only one station stop sign for any train. Else there are two or more station stop signs that apply to:
- Trains with the number of cars stated at the sign
- Trains with the length stated at the sign
- Trains with the number of wheel axles stated at the sign
- Any of the 3 alternatives above combined with a specific type/class of train/vehicle
The most common alternative in BVE is the 1st: Number of cars. Info on the number of cars in the simulated train is often displayed in the info shown when train is selected for the simulation, se chapter 2.2 Select line and vehicle, picture 4.
3.1.2.3 Stop signs
The function of stop signs is similar to the function of the station stop signs. The difference is that stop signs not mark locations for passengers to embark/disembark. Such locations may be where freight trains should stop or trains stop at storage tracks etc.
3.2 Japan
3.2.1 Light signals
Japanese light signals may be attached more than one to a mast. In this case, signals apply to tracks in the same order, as they are located on the pole.
3.2.1.1 Main signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Proceed |
|
|
Proceed at maximum 75 km/h |
|
|
Proceed at maximum 55 km/h |
|
|
Proceed at maximum 25 km/h |
|
|
Stop! |
3.2.1.2 Approach signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Next main signal indication is Proceed |
|
|
Next main signal indication is a speed restriction (75, 55 or 25 km/h) |
|
|
Next main signal indication is Stop! |
|
|
Next grade crossing signal indication is Movement allowed |
|
|
Next grade crossing signal indication is Stop! |
3.2.1.3 Other light signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Movement allowed (grade crossing signal) |
|
|
Stop! (grade crossing signal) |
3.2.2 Sign signals
3.2.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Maximum speed 75 km/h |
|
|
Maximum speed 25 km/h at the track to the left |
|
|
Maximum speed 35 km/h at the track to the right |
|
|
No speed limit at the track. Maximum speed for the vehicles in the consist applies |

|
Temporary speed restriction of 70 km/h follows |

|
Temporary speed restriction, maximum speed 70 km/h |
|
End of temporary speed restriction (previously by light signal or sign signal signaled maximum speed applies) |
3.2.2.2 Station stop signs
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Stop position for all trains |
|
|
Stop position for trains with the number of cars stated on the sign |
3.2.2.3 Other sign signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Beginning of line using ATS-P |
|
|
Name of next station |
3.3 USA
3.3.1 New York Subway
The New York subway was previously owned by 3 companies each of them with its own line network and to some extent different signal systems. Because of this, there are still 2 somewhat different sets of signal aspects in use in the New York subway.
Those who have created New York subway lines for OpenBVE have had different ambitions in making the signals in those routes looking as in the real subway. Do not be surprised if you in some of these routes find signals following not any of the New York signal systems but rather the Japanese signal system (see chapter 3.2 Japan).
3.3.1.1 Light signals
3.3.1.1.1 Main signals
There are 2 kinds of main signals: Those who are at locations where it is, at least, one turnout making it possible to proceed into different routes. The other kind of main signals are found at all other locations.
The light signals at locations with more than one possible route to proceed at are in most cases made of 2 1/2 signal heads above each other:
- Den top signal head indicates stop, proceed etc. as light signals usually do
- The next signal head indicates which route is set to proceed at:
- Green light indicates a route set straight ahead or at the main track
- Yellow light indicates a route set to a diverging track
- Red light is shown if the top signal is indicating stop
The bottom signal head has only one light (yellow). This part of the signal is rarely found in OpenBVE, and if it is there, it is never lit. Because of this, that bottom signal head and aspects where it is showing a yellow light are omitted from the tables below.
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
| Proceed | |
| Proceed; be prepared to stop short of nest main signal | |
| Stop! | |
| Proceed at the main route | |
| Proceed at a diverging route | |
| Proceed at the main route; be prepared to stop short of next main signal | |
| Proceed at a diverging route; be prepared to stop short of next main signal | |
| Stop! |
On some lines in the New York subway, which once in a time belonged to the company IRT another set of signal aspects are used at locations with more than one possible route to proceed at. The main signal is made of 2 signal heads above each other. The top signal head signals the main route, the bottom signal head signals the diverging route.
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
| Proceed at the main route | |
| Proceed at a diverging route | |
| Proceed at the main route; be prepared to stop short of next main signal | |
| Proceed at a diverging route; be prepared to stop short of next main signal | |
| Stop! |
3.3.1.1.2 Other light signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
| Stop! This kind of signal never shows any other aspect |
3.3.1.2 Sign signals
3.3.1.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
Permissible speed indicators indicate speed in mph. For some reason, some of the trains in OpenBVE for the New York subway have speedometer indication in km/h.
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
| Permissible speed 35 mph | |
| Permissible speed 35 mph at the diverging track | |
| Permissible speed 15 mph, if exceeded next main signal or the main signal after the next, will indicate stop. Should a train occupy the track just beyond any of these signals, they will show stop even if the permissible speed is not exceeded. | |
| If next main signal is indicating stop, proceed at no more than 15 mph. If not exceeded, that main signal will change aspect to yellow. If this happens be prepared to stop short of a train occupying the track beyond that yellow main signal. | |
| If next main signal is indication stop and under that signal are lit a number indicator, proceed from the T-sign a no more than the speed in mph indicated by the lit number indicator. If not exceeded, that main signal will change aspect to yellow. If this happens be prepared to stop short of a train occupying the track beyond that yellow main signal. | |
|
|
End of speed restriction. The lowest of either the permissible speed for the vehicles in the train or a general permissible speed for the line applies. |
|
|
End of speed restriction. Trains with the number of cars (or a less numbers of cars) indicated at the sign may from the location of the sign increase its speed to the lowest of either the permissible speed for the vehicles in the train or a general permissible speed for the line. |
3.3.1.2.2 Station stop signs and stop signs
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
| Stop position for all trains | |
Stop position for all trains operated by the motorman alone (no
conductor). OPTO is an abbreviation of One Person Train Operation |
|
|
|
Stop position for trains with the number of cars indicated on the sign |
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Stop position for trains with the number of cars indicated at the sign at other locations than station platforms (such as storage and lay-up tracks). |
3.3.1.2.3 Other sign signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
| Below a light signal: Not possible, even at lowest speed, to proceed beyond this signal while it is indicating stop. | |
| Switch train radio channel to the channel indicated on the sign (in this case radio channel B2) |
3.3.2 Railway lines
3.3.2.1 Light signals
American light signals may be made of 2 signal heads on the same mast, one above the other. In this case, the top signal signals the main route and the bottom signal signals a diverging route. This configuration with 2 signal heads may also be used for exit signals.
3.3.2.1.1 Main signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Proceed |
|
|
Proceed at maximum 55 km/h, be prepared that next main signal indicates stop |
|
|
Stop! |
3.3.2.2 Sign signals
3.3.2.2.1 Permissible speed indicators
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Permissible speed 80 mph |
|
|
Yard: Use the bell while moving, permissible speed 15 mph |
3.3.2.2.2 Stop signs
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Stop position for all trains |
3.3.2.2.3 Other sign signals
| Aspect | Indication |
|---|---|
|
|
Sound the horn before a grade crossing: 2 long sounds, one short sound and a long sign prolonged until the train is in the grade crossing |
|
|
End of yard: You may stop the bell ringing |


 © Patrick Norqvist
© Patrick Norqvist